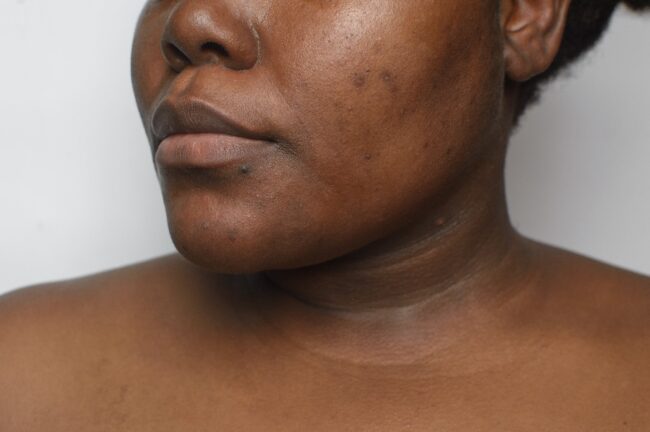
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition characterized by the darkening of specific areas of the skin. It occurs when an excess of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, eyes, and hair, is produced in these areas. While hyperpigmentation is generally harmless, it can be a cosmetic concern for many individuals. Dr. Jason Emer, MD, reviews its causes, types, and treatments, which are essential for effectively managing this condition and achieving clearer, more even-toned skin.
What is Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation appears as darkened patches or spots on the skin that make it look uneven. These patches can vary in size and may develop anywhere on the body. While hyperpigmentation itself is not usually a serious medical issue, it may indicate an underlying health condition in some cases. For many people, however, it is primarily a cosmetic issue that can affect self-esteem and confidence.
Causes of Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation can result from a variety of factors, including:
- Sun Exposure: The most common cause of hyperpigmentation is prolonged exposure to the sun. Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun can accelerate melanin production, leading to sun spots or age spots, which are forms of hyperpigmentation.
- Inflammation: Any condition that causes skin inflammation, such as acne, eczema, or psoriasis, can lead to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). This occurs when the skin heals after an inflammatory wound and leaves a dark spot.
- Hormonal Changes: Conditions such as melasma are often triggered by hormonal changes. Melasma, also known as “the mask of pregnancy,” commonly occurs in pregnant women due to increased estrogen levels. Hormonal contraceptives and hormone replacement therapy can also trigger melasma.
- Medical Conditions and Medications: Certain medical conditions like Addison’s disease, which affects the adrenal glands, can increase melanin production, leading to hyperpigmentation. Additionally, some medications, including chemotherapy drugs, antibiotics, and anti-seizure medications, can cause hyperpigmentation as a side effect.
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals are genetically predisposed to hyperpigmentation. Those with darker skin tones are more prone to this condition because they have more melanin in their skin.
Types of Hyperpigmentation
Understanding the different types of hyperpigmentation can help in selecting the most effective treatment:
- Melasma: Melasma is characterized by brown or gray-brown patches, usually in facial areas like the cheeks, forehead, bridge of the nose, and chin. This type of hyperpigmentation is primarily caused by hormonal changes and sun exposure.
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): PIH occurs when the skin darkens after an inflammatory reaction, such as acne, eczema, or injury. This is more common in people with darker skin tones.
- Sun Spots (Lentigines): Also known as liver spots or age spots, sun spots are small, darkened patches on the skin caused by long-term sun exposure. They are commonly found on the face, hands, shoulders, and arms.
- Freckles: Freckles are small brown spots on the skin that become more pronounced with sun exposure. Unlike other forms of hyperpigmentation, freckles are typically genetic and more common in people with fair skin.
Treatment Options for Hyperpigmentation
Treating hyperpigmentation involves a combination of topical treatments, medical procedures, and lifestyle modifications. The choice of treatment depends on the type and severity of hyperpigmentation.
Topical Treatments
- Hydroquinone: This is a popular skin-lightening agent that reduces the production of melanin. It is available over the counter in lower concentrations, but higher concentrations require a prescription. Prolonged use can cause skin irritation, so it is best used under the guidance of a dermatologist.
- Retinoids: Retinoids, such as tretinoin, help increase cell turnover, thereby promoting the shedding of pigmented skin cells. They are effective but can cause dryness and irritation, especially in individuals with sensitive skin.
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that can inhibit melanin production and brighten the skin. It is commonly found in serums and creams and is suitable for daily use.
- Azelaic Acid: Azelaic acid helps reduce pigmentation and has anti-inflammatory properties, making it suitable for treating both melasma and PIH. It is less irritating than hydroquinone and retinoids.
- Kojic Acid: Derived from fungi, kojic acid helps lighten pigmentation by inhibiting the production of tyrosinase, an enzyme involved in melanin production. It is often used in conjunction with other treatments.
Medical Procedures
- Chemical Peels: Chemical peels involve applying a solution to the skin that causes it to exfoliate and eventually peel off, revealing new, lighter skin underneath. Peels come in varying strengths, and the choice depends on the severity of hyperpigmentation.
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatments target and break down the excess melanin in the skin. Different types of lasers are available, such as fractional lasers and intense pulsed light (IPL). Laser therapy can be effective but may require multiple sessions.
- Microdermabrasion and Dermabrasion: These procedures involve exfoliating the skin to remove the upper layers of dead skin cells, which can help reduce pigmentation. Dermabrasion is more intense than microdermabrasion and requires more recovery time.
Lifestyle Modifications and Prevention
- Sun Protection: Proper sun protection is crucial for preventing and managing hyperpigmentation. Wearing broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding sun exposure during peak hours can prevent further darkening of pigmented areas.
- Avoid Picking or Scratching the Skin: For those with PIH, it is important to avoid picking or scratching the skin, as this can worsen hyperpigmentation and lead to more dark spots.
- Healthy Diet and Skincare Routine: A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, along with a consistent skincare routine, can help improve overall skin health and reduce the risk of hyperpigmentation.
Hyperpigmentation is a common and generally harmless skin condition, but it can be distressing for those who experience it. Understanding the underlying causes and types of hyperpigmentation is essential for selecting the most effective treatments. With a range of topical treatments, medical procedures, and preventive measures available, it is possible to manage hyperpigmentation effectively and achieve a more even skin tone. Consulting with a dermatologist is always recommended for personalized treatment plans tailored to individual skin types and conditions.